Helping teachers to exploit the pedagogical potential of their Learning Management System
Abstracting the technical design domain of LMSs in order to specify soundly and executable learning scenarios
Nowadays, LMSs are widely spread in academic institutions and not restricted to distant courses but are also useful during or in complement to face-to-face learning sessions. Design skills can be acquired through specific teacher education programs, often focusing on the features and technical aspects of the platform. Few courses deal with how to design pedagogically sound learning situations. Teachers develop ad hoc and individual learning design techniques by diverting and experiencing combination of LMSs’ features and functionalities. In such context, it is relevant to help teachers in focusing on pedagogical aspects and their instructional design setting-up for the specific LMS they have at their disposal. A focus on the instructional design possibilities and how they can rely on the platform features should encourage individual and collective understanding about the pedagogical uses of the targeted LMS. Our aim is to provide teachers with some graphical instructional design languages, and their dedicated authoring-tool, in order to specify pedagogically sound learning scenarios that can be technically executable for automatically setting-up upon their LMS.
Modeling and abstraction for a specific LMS-centered approach
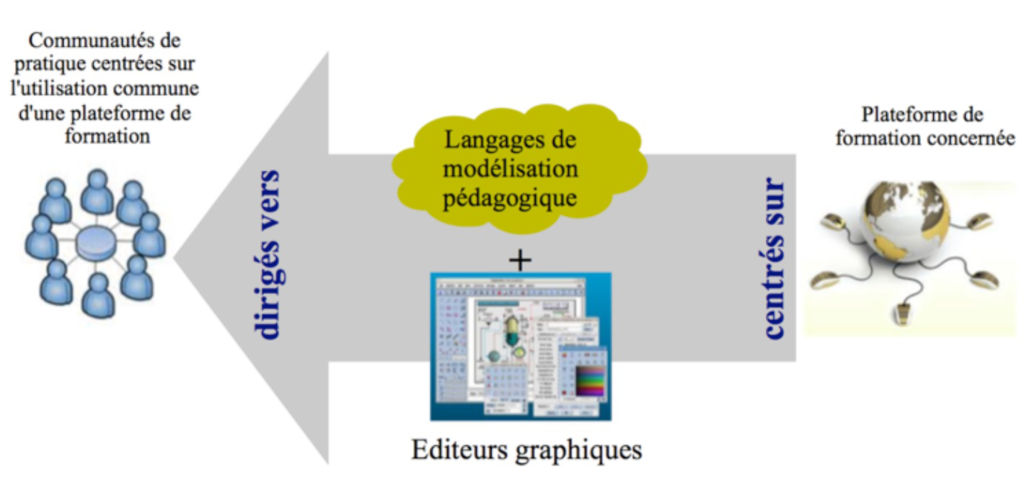
Current learning design approaches propose learning design languages independent from any LMSs. This orientation meets the need for pedagogical expressiveness but encounters difficulties in the handling and machine execution of the produced learning scenarios: the matching towards the technical features provided by an LMS result with more or less information and semantics losses depending on the initial gap between both languages and platform instructional design domains. On the contrary, we propose to identify, make explicit, and formalize the implicit instructional design domain of LMSs. Then, we abstract it in order to extend the pedagogical expressiveness with some new concepts and properties we are able to match, by construction. Our instructional design languages are LMS-centered, i.e. specific to an LMS. Produced learning scenarios will be automatically executed as source information for setting-up the equivalent LMS course thanks to a specific API. The Model Driven Engineering and Domain-Specific Modeling theoretical and practical frameworks are used to achieve our objectives.
We proposed a method to identify and formalize the implicit learning design domains from LMSs as metamodels. We explored an extension approach from this metamodel by enriching it with some new activities embedding recurrent pedagogical uses designers can perform from specific LMS features. Combined with an appropriated graphical notation, we elaborated from this new metamodel an instructional design language for the Moodle platform. We developed an editor that provides an export format conformed to the initial metamodel: teachers can import these scenarios via an added import plugin upon the LMS.
The GraphiT project has been a great opportunity to bring together teachers-researchers with different research orientations (Requirements Engineering, Model Driven Engineering) on a shared research object (LMSs) and cross-topics (instructional design and operationalization). Many scientific communications have been produced and presented for both a national and an international audience.
The GraphiT young researcher project has followed a design-based research methodology. It involved several researchers from the IEIAH team of the LIUM computer-science laboratory (Le Maine University). The project started in February 2012 for 44 months. It has been fully funded by the ANR agency (157 568 €).
 Nour El Mawas
Nour El Mawas Sébastien Iksal
Sébastien Iksal Pierre Laforcade
Pierre Laforcade Lahcen Oubahssi
Lahcen Oubahssi Claudine Piau-Toffolon
Claudine Piau-Toffolon
 Français
Français

